This article is adapted from an episode of our podcast “Civic.” Click the audio player below to hear the full story.
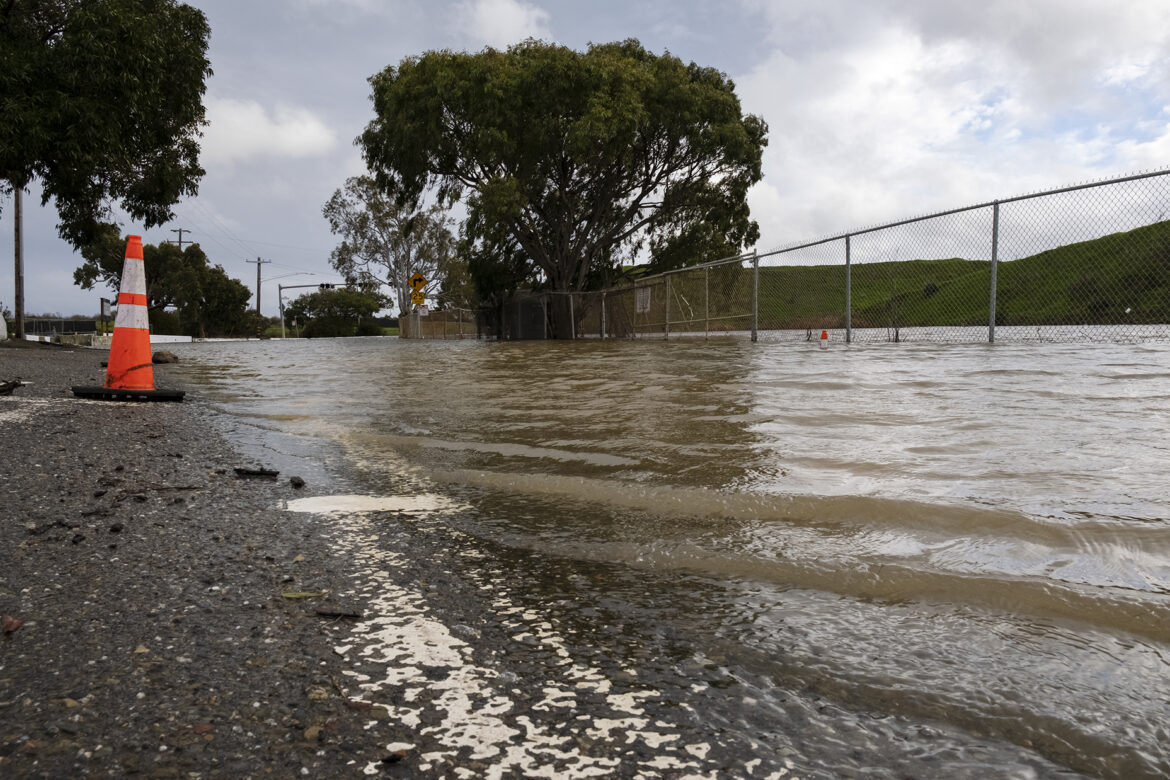
Rains this winter and early spring ended the drought in the Bay Area and brought a kind of weather whiplash that put San Francisco’s Department of Emergency Management to the test.
Early in the storm cycle, the department faced challenges communicating with the public, especially with people experiencing homelessness. Internal confusion over the forecast delayed the opening of its Emergency Operations Center until a major storm was under way. In at least one instance, flood barriers were deployed too late to prevent homes and businesses from being inundated.
Despite those missteps, the city rallied a coordinated response from its Emergency Operations Center, where multiple city agencies, along with Pacific Gas and Electric Co. representatives, gathered to discuss and act on emerging issues in real time.
It has been years since California faced this kind of barrage. The National Weather Service said that at least 14 powerful atmospheric rivers have slammed into California since October, triggering flooding and downing trees that have killed at least 22 people statewide, including two who were struck by falling trees in San Francisco.
And there could be more trouble to come: The Sierra snowpack is at a staggering 225% of normal, and while it will fill reservoirs, a fast spring melt could cause even more flooding.
In a new “Civic” episode, we examine how the city responded to the first big deluge of the season and what it learned from that harried experience to improve response to subsequent storms.
The biggest rainstorm hit San Francisco with 5.5 inches of rain on New Year’s Eve, when many city employees were away on vacation. Adrienne Bechelli, deputy director of San Francisco’s Department of Emergency Management, said city departments were able to mount a full response despite being short staffed.
“The city tasks that were the most urgent priority were, of course, flood mitigation and clearing catch basins ensuring that all of our storm drains were clear,” she said.
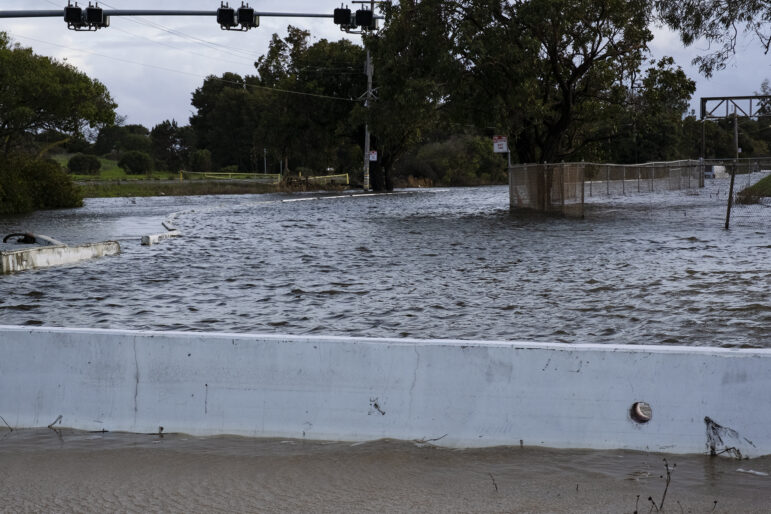

Yesica Prado / San Francisco Public Press
After a series of atmospheric river storms hit California in early January, Gilman Avenue is flooded under nearly three feet of water near where it turns into the Hunters Point Expressway.Emergency response teams also helped drivers whose vehicles were stranded in floodwaters and worked to get people living on the streets into emergency shelters, she said.
Despite those efforts, some residents and businesses in the Mission District said the city was slow in providing information and failed to put up additional flood gates as it has done before previous storms.
Blame game
On Jan. 3, Mayor London Breed began a news conference saying the city didn’t expect so much rain.
“We were under the impression and notified by our National Weather Service that we could anticipate not even an inch of rain,” she said. Less than one inch of rain is not considered a threat according to the city’s winter storm and flood plan.
Mary Ellen Carroll, the executive director of the Department of Emergency Management, echoed the mayor’s claims and said the city scrambled to increase its response on New Year’s Eve: “Our city employees rallied and we activated our Emergency Operations Center late morning when we realized what was actually happening was a little different than the actual forecast.”
Brian Garcia, the warning coordination meteorologist for the National Weather Service in the Bay Area, disputed those claims. He said the forecast showed a strong system hitting San Francisco days before it arrived.
“We started messaging that on the 26th and 27th, when we started putting out information for the New Year’s Eve system,” he said. “We issued a flood watch on December 28. So, we definitely saw something coming in.”
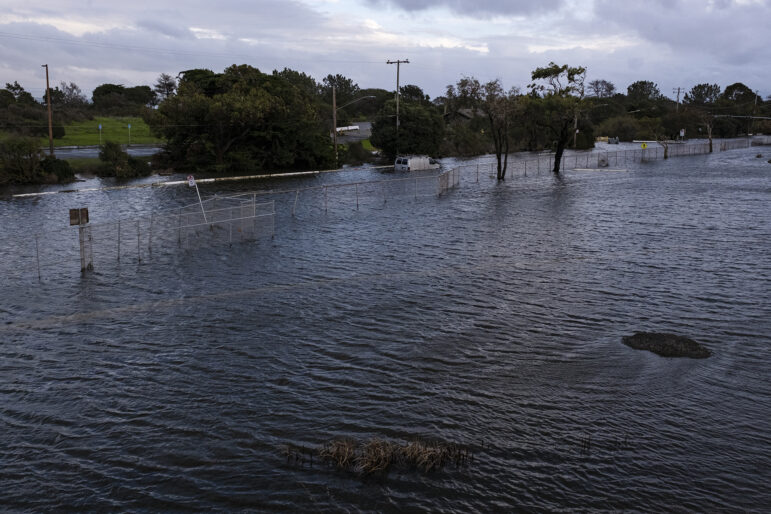

Yesica Prado / San Francisco Public Press
The entrance to San Francisco’s Vehicle Triage Center, where the city allows people to live in cars and RVs, was flooded by Dec. 31, 2022, public records show. The city did not immediately respond to reports of flooding near the former Candlestick Park by the Hunters Point Expressway, which was submerged under 32 inches of water on Jan. 13, 2023. “We’re growing concerned that emergency services will not be able to access the site if needed,” wrote Louis Bracco, manager at Community Housing Partnership.The weather service issues flood watches when the risk of a hazardous weather or flood event increases significantly.
San Francisco’s own response protocol lays out an elaborate system to prepare for major storms. The city activated its emergency response on Dec. 28, after the National Weather Service issued its flood watch 96 hours ahead of the storm.
Garcia said city leaders’ forecast concerns seemed to center on whether the New Year’s Eve fireworks show — which had been cancelled during the first two years of the pandemic — could proceed as planned over the bay near the Embarcadero.
“There was a focus for all of us to see if the rain was going to clear out by then, on the briefing that we provided on December 28,” Garcia said. “We were talking about the wind and the rain across our entire area, including the city, and how nasty it was going to be. The fireworks were definitely a bit of a focus.”
The city seemed to have moved past the “one inch of rain” forecast claim in late February, when Bechelli said the forecast didn’t hamper the city’s efforts.
“We were full out in terms of our operational response,” she said, shifting the focus to the city’s storm water capacity. “The built infrastructure of San Francisco is not built to handle five and a half inches of rain in a 24-hour period — we’re going to see inevitable flooding.”
Garcia is ready to move on. “You’re always learning how to communicate better,” he said. “We continue to look forward to many years of a strong partnership with the great city of San Francisco.”
A representative from the Department of Emergency Management wrote in an email that the city hopes to bring National Weather Service representatives into the Emergency Operations Center during future storms.
Seeking shelter
Following the New Year’s Eve storm, San Francisco Public Press reporters Yesica Prado and Madison Alvarado visited eight San Francisco neighborhoods over three days to talk to homeless people out in the rain.
Prado said that access to shelters varies a lot by neighborhood.
“Some places, like in the Bayview, people are able to be more settled down versus being in the Civic Center or being in Japantown, where people are constantly on the move, and they will have to seek shelter if they want accommodations for the night,” she said.

Yesica Prado / San Francisco Public Press
A man camps near a convenience store on Franklin Street in San Francisco on Jan. 14, 2023. The sloped street carries rainwater toward his sleeping quarters. He tucks wet clothes inside his tent before stepping out for the day.Alvarado said nonprofits were scrambling to find spots for people and, in some cases, sent them across the city where there were beds available.
“We were visiting a shelter and dining room down in the Bayview. We actually heard that at the end of the day the St. Anthony Foundation bused people down to Mother Brown’s in the Bayview, because they knew that there were shelter options down there,” she said.

Yesica Prado / San Francisco Public Press
A worker scoots down Polk Street through the Lower Nob Hill neighborhood to deliver food in the rain on Jan. 14, 2023. On the same block, a wheelchair user rolls past the Next Door Shelter, which increases its bed capacity during inclement weather.San Francisco added more beds to all its shelters in anticipation of a demand surge and worked with nonprofits and churches to add more, but Alvarado said finding information about where beds are available can be difficult for people without access to the internet.
“If you don’t have a phone, you don’t know where you can go because you don’t know where they are,” she said. “Maybe you know of another shelter, but you don’t know how to get there.”
During their reporting, they came across a man shivering on the sidewalk.
“We noticed that nobody had actually approached him,” Prado said. “We didn’t ask for an interview. We went to ask ‘do you need any help?’ And then all he could muster is that, yeah, like he was cold. So we went back to our car, and we got some supplies for him, some dry clothes. But once we came back, he wasn’t really responsive. And that’s when we thought, he really needs some other kind of help.”
Prado and Alvarado said they looked online to see whom they should call. The Healthy Streets Operation Center website indicated that calls from concerned citizens would not be returned. Prado and Alvarado were reluctant to call 911, which they said they thought might bring a police response to a medical issue. So, they ended up calling 311, and a team designated to help homeless people showed up a few minutes later.
Confusion over whom to call was understandable. During the Jan. 3 news conference, San Francisco Fire Chief Janine Nicholson discouraged people from using 911 for anything less than an emergency.
“I can’t stress it enough,” she said. “Call 911 for life threatening emergencies only. We still have to run all of our critical 911 calls, whether it’s a cardiac arrest or a car accident or a fire.”
But Bechelli said that calling 911 is the right choice: “Our 911 dispatchers are trained to send the right resource for that particular problem. If there is a medical emergency, they will send a medical response in order to help that person.”
Encampment sweeps continued
Representatives from the Department of Emergency Management said that they reached out to people in encampments to offer them shelter ahead of and during the rain storms, and in some cases, to warn them that the place they were in was prone to flooding or other dangers. Meanwhile, the Department of Public Works continued to dismantle tent encampments during the inclement weather, as witnessed by our reporters.
Alvarado spoke with a man named Duane who said he had been camping on 19th Street near Harrison Street for about a month, and that city workers kept asking him and other people nearby to move.
“They were making us move every week, every week, back and forth, back and forth. No matter if it was raining,” he said.
Our reporters said the city was offering temporary shelter stays to people in the two encampments they visited, but few of the people they spoke to said they were taking the offers.
Duane said he thought congregate shelters and even navigation centers, which allow groups of friends to stay together, were too dangerous. “You got to deal with a bunch of crazy people. They pick fights with literally no reason,” he said. “It’s like, yeah, they offer you housing. But you gotta jump through hoops to get in.”
Mitigating floodwaters
The city has long known where flooding is most likely to happen and has some plans to mitigate it. After the December and January storms, residents and businesses affected by flooding were asked to fill out questionnaires to help the city track damage and potentially help San Franciscans get federal relief.
Bechelli said 117 people submitted responses about flooding affecting their homes and 17 submitted responses about their businesses. Many responses came from people in the Marina, Mission, Bernal Heights, Glen Park, Castro, Potrero Hill and Dolores Heights neighborhoods, she said.
Most had flood damage, but few had flood insurance. The Federal Emergency Management Agency declined to offer emergency grants to those affected, but will offer Small Business Administration Disaster Loan assistance. Applicants must apply in person at the War Memorial building on Van Ness Avenue.
The city has plans to address some areas prone to flooding. The San Francisco Public Utilities Commission has allocated $632 million for three large drainage projects in low-lying areas.
- The Wawona Street Stormwater Project in West Portal will be under construction until 2024.
- The Lower Alemany Area Rainwater Improvements Project in Bernal Heights will improve stormwater management near the Alemany Farmer’s Market, and the Interstate 280 and U.S. 101 interchange in Bernal Heights. Construction isn’t expected to begin before 2025 with completion in 2028.
- The Folsom Area Stormwater Improvement Project would cover multiple streets in the Mission to reduce flooding in one of the neighborhoods hardest hit in even moderate storms. The project is in the planning phase with no date set for construction to begin.
In a more modest effort, the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission has distributed $2.5 million in grants to schools and nonprofits to fund rain gardens, green roofs and other green infrastructure projects to help slow down and redirect floodwaters.
Weather response report card
So, how did the city respond to our wild and wet winter?
There were communication problems.
It’s unclear why city officials and the national weather service got into an argument over the New Year’s Eve forecast. Confusion over the forecast delayed the opening of the city’s Emergency Operations Center.
Given conflicting instructions, San Franciscans may have been confused about when to call 911, especially around helping homeless people.
Finding information about shelter locations generally requires access to a smartphone or the internet. Direct outreach to the homeless is limited by staffing constraints and the fact that those needing the information move around a lot.
Overall, the city’s response to protecting people in need was hampered by the same factors that have led to so many people living on the streets: a lack of long-term housing and a focus on temporary shelters, which are often considered by the homeless to be worse than staying outside.
The city knows where the most problematic flood areas are and has plans to mitigate many of them, but those infrastructure projects are years from completion.

Yesica Prado / San Francisco Public Press
A pedestrian crosses Harrison Street in the Mission District in the rain on Jan. 14, 2023.The New Year’s Eve storm was the city’s second wettest on record, only surpassed by a Nov. 11, 1994, storm that brought 5.54 inches of rain to San Francisco. It is too early to know whether California will break its previous record set in 1952-53 for wettest season based on snowfall. The total snowpack results are usually measured and reported April 1.
Inconsistent weather patterns
For the last few years California has been experiencing a series of La Niña weather patterns, which normally mean drier than usual conditions. An El Niño pattern usually means a wetter than average winter. But within those two major patterns are lesser intra-seasonal oscillations that can change from month to month. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration explains that variations in tropical rainfall can shift the wintertime jet stream and atmospheric circulation over the North Pacific and western North America, thereby overriding the dominant seasonal weather pattern.
The weather service’s Garcia explains that if the intra-seasonal oscillations “all come together in the right way, they can override a strong entrenched signal. We can have El Niño years that are extremely dry. And conversely, we can have La Niña years that are extremely wet. It’s not unheard of, it’s just not the norm.”
The La Niña pattern officially ended March 9. It’s unclear whether we’ll see an El Niño pattern by next fall or a neutral pattern.
“In California, we typically end major droughts with major floods,” Garcia said. “This has happened multiple times throughout California’s history. So, is this related to climate change at all? The way that it’s related to climate change are the extremes at which we’re seeing those higher heights and lower lows. It’s not happening any more frequently than historically, it’s just getting deeper and higher at the same time.”
CLARIFICATION 4/10/23: The Department of Emergency Management responded to this story to characterize the changing activation status of its Emergency Operations Center. Though only described as “open” during specified times, it is otherwise continuously in standby mode and monitoring events.